Almost all Lenovo smartphones are powered by MediaTek processors, which means that gadgets with such a chipset always have the Lenovo engineering menu. Today we will tell you how to go there, what it is needed for and how any owner of a Lenovo gadget can use it to their benefit.
You probably already understood from the name that this menu was created in order to configure, test and debug various phone modules. Since it is mainly used for the latter purpose, the average user will not be interested in digging into at least half of these functions.
In addition, we urge you to be careful: if you do not know what exactly you are doing, then it is better not to mess with this setting, as there is a risk of disabling important parameters of the device or even turning it into a “brick”.
Entering the Lenovo engineering menu
To log in, you need to open the dialing menu on Lenovo and dial a special code: *#*#3646633#*#*. True, it doesn't always work. If nothing happens, try entering *#*#4636#*#* or *#15963#*. If everything is done correctly, you will see the Engeneer Mode program with a slightly strange design - this is the same engineering menu.
If for some reason not a single code worked, then to enter the section we need, use the specialized program “MTK Engineering Mode” or another similar one. To do this, you will need to go to the Play Market or App Store and download it. Once it is installed, launch the application and complete all the necessary steps. As a result, you will be able to configure the phone through the engineering menu by going to certain sections of it.
How to unlock an Android smartphone
Use the Smart Lock feature
When enabled, this feature automatically unlocks your screen when at least one of the conditions you specify is met. For example, if the device is located at your home or another device of yours is connected to it via Bluetooth.
You may have previously set up Smart Lock but forgot about it. In this case, remember the given condition and fulfill it. For example, if you have added one of the Bluetooth devices to the list of trusted devices on your smartphone, turn on the wireless module on both. Once connected, the phone can be unlocked without entering a PIN, password or key.
If Smart Lock has not been configured in advance or you cannot meet the specified condition, then this method is not suitable.
Bypass protection using Google Account
Some devices with older versions of Android (before 5.0 Lollipop) allow you to bypass the screen lock using your Google Account. But for this, the device must be connected to the Network. To check if your smartphone supports this method, enter any password, PIN or pattern five times.
After five incorrect entry attempts, the message “Forgot your password?” should appear on the screen. or similar hint. Click on this inscription and enter the username and password for the Google account that is the main one on your smartphone. After successfully logging in, you can specify a new password or set up a different screen lock method.
If you also forgot your Google account password, try to restore access to it using the company’s special service.
3. Use the service from the smartphone manufacturer
Some brands offer owners of their devices additional unlocking tools. For example, Samsung has a Find My Mobile service, with which you can remove a pattern, PIN code, password, and even a fingerprint. To do this, your device must be linked to your Samsung account, support the service, and be online.
To find out whether such services exist for your model, look for this information in the instructions or on the manufacturer’s official website.
Reset the device to factory settings
If other options do not work, all that remains is to return the factory settings. This will lead to the loss of all data, copies of which are not saved in your Google account and other cloud services. But you can remove the protection from the screen.
Turn off your smartphone and remove the memory card if it was inside. Then try these key combinations in turn until one of them works (you need to press all the buttons and hold them for about 10-15 seconds):
- Volume down key + power button;
- Volume up key + power button;
- Volume Down key + Power button + Home key;
- Volume down key + Volume up key + Power button.
When the service menu appears on the display, select Recovery, and then the Wipe data / factory reset command. If none of the key combinations work or you don't see the necessary commands in the menu, look for reset instructions specific to your device model.
After this, the smartphone should return to factory settings within a few minutes. The device may request a login and password from a previously connected Google account, but you will no longer need to unlock the screen. After logging into your old account, the system will restore the settings and data synchronized with it.
All of the unlocking methods listed above are suitable not only for smartphones, but also for Android tablets.
Engineering menu functionality
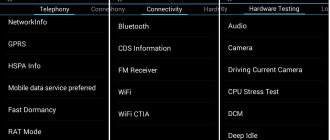
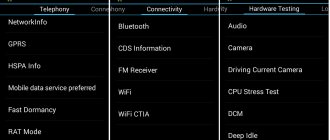
There are several hundred different settings hidden here, which are divided into six large tabs:
- Telephony – view and check the parameters of the phone’s mobile network, set automatic answering of an incoming call, check the compatibility of the smartphone with a specific mobile operator, disable support for bands, and it is also possible to reset all settings to factory settings;
- Connectivity – checking Wi-Fi and Bluetooth module, function to turn off the display while using Wi-Fi Display and much more;
- Module testing (Hardware Testing) - test the sound volume through the headset, increase it, check the screen and other important sensors and modules of the Lenovo gadget;
- Location – all the same actions, but related to location verification: disabling A-GPS detection and others;
- Debugging (Log & Debugging) – here, for the most part, various links to utilities and tests from MediaTek and those companies that supply other components to the smartphone are stored;
- Others – other settings and tests, for example, setting font sizes on the phone.
It would also be useful to clarify that setting up the phone through the engineering menu on new Lenovo models will be carried out a little differently due to the different structure of the menu items, however, the general meaning remains the same, and therefore it will not be difficult for a knowledgeable person to configure it. Lenovo service codes for entering the menu may differ slightly from what was indicated in the previous paragraph, but usually it is the same.
Lenovo secret codes
* # 06 # query string of the phone number.
# # # # 1040 # check network status information; View Local CELL Lane rxlev (mobile signal reception parameters) normally between -80 to 87.
# # # # 1111 # Right-click the phone's screen colors, tones, vibration, keyboard performance testing.
# # # # 7777 # phone restore factory settings.
# # # # 0000 # check the phone's software version; such as 40411.
# # # # 2222 # Lookup Cell Phone SN as 6162.
# # # # 4444 # phone automatically restart.
# # # # 88 ** # Right function MONTERNET and players to switch between.
# # # # 99 ** # JAVA folder will exist Carry the JAR and JAD files copied to the phone system to complete the installation of JAVA card.
* # 0000 # query software kernel version as AE23 AE06.
# # # # 11 # network time synchronization.
# # # # 1001 # Unicom network lock feature (currently if there is no such function)
# # # # 10086 # mobile network lock feature (currently if there is no such function)
On this page you will find the secret codes for Lenovo Vibe Shot. With their help, you can access advanced settings, use the h > The IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity) is a unique number to identify GSM, WCDMA, and iDEN mobile phones, as well as some satellite phones. The IMEI is only used for identifying the device and has no permanent or semi-permanent relation to the subscriber. Number is used by the GSM network to identify valid devices and therefore can be used for stopping a stolen phone from accessing the network in that country.
I forgot my Lenovo pattern key. What to do?
The security system on Android Lenovo smartphones allows you to install a simple, but at the same time effective, pattern key on them, which provides it with protection from unwanted attacks on personal information. But it happens that your memory fails and you cannot remember it, being left alone with only a beautiful “piece of plastic” in which your blocked data is stored. How to remember a forgotten pattern key on Android or what to do to unlock your smartphone?
Method 1: Try to reset your password.
One of the ways to unlock a smartphone after a forgotten pattern key is to reset the security measures by logging into the device using the Google account that is registered on the phone.
The peculiarity of this method is that to unlock it, it is necessary that there is at least some connection to the Internet (Wi-Fi or mobile Internet) on the phone.
If the Internet is working and your Google account is confirmed, you will immediately be able to change the existing key or completely disable the phone locking service.
Method 2 - data reset with complete loss of information.
If you still can’t recover your password by entering your Google account, the most radical method is a hard reset. It is worth paying attention to the fact that with a hard reboot, you will lose all the information stored on your device in the internal memory: photos, videos, various documents, SMS, address book contacts and other materials.
To learn how to do a hard reset (full reset) on your phone, read the article: how to do a Hard Reset on Lenovo
Detailed technical specifications
Make and model
Make and model of the device, and alternative names (if any).
| Brand Device manufacturer company. | Lenovo |
| Model Device name. | K13 Note |
Design
Appearance of the device including dimensions, weight, volume, colors and materials.
| Width The horizontal side of the device when used in standard orientation. | 75.73 mm (millimeters) |
| Height The vertical side of the device when used in standard orientation. | 165.22 mm (millimeters) |
| Thickness The cross-sectional size of the device. | 9.19 mm (millimeters) |
| Weight How much does the device weigh excluding the case, SIM and memory cards and other additional elements. | 200 g (grams) |
| Volume Approximate value calculated using the formula: length times width times height. | 114.99 cm³ (cubic centimeters) |
| Colors What colors is the device available in? | Pearl Sakura Aurora Gray |
| Housing materials What materials is the body made of? | Plastic |
System on a Chip (SoC)
A system on a chip, a single-chip system (System on a Chip, SoC) is when several systems performing different device functions are connected on one chip.
| System on a Chip (SoC) A single-chip system that contains components such as a processor, graphics accelerator, memory units, communication interfaces, etc., as well as software for the operation of the system. | Qualcomm Snapdragon 460 |
Central processing unit (CPU)
| Central processing unit (CPU) The main component of the device is responsible for calculations and data processing. | 4x 1.8 GHz Cortex-A73, 4x 1.8 GHz Cortex-A53 |
| Technical process What technological process is used to make the chip? The smaller the process technology, the better - the chips consume less power and generate less heat. | 11 nm (nanometers) |
| Processor size Processor capacity is a parameter that indicates how many bits of data a processor register processes in 1 clock cycle. This is usually 32 or 64 bits. | 64 bit |
| Instruction Set Architecture Instruction set architecture (ISA) is a programmable part of the microprocessor core used by software to control the operation of the processor. | ARMv8-A |
| Number of processor cores The processor can be either single-core or multi-core. The performance of the processor depends on the number of cores (threads). The more cores working simultaneously, the higher the power consumption, so in mobile devices all cores are used only under high load. | 8 |
| CPU clock speed Clock speed is the number of operations per second that a processor or its core can achieve. The higher the frequency, the higher the overall performance of the device, but performance also depends on the processor architecture and the number of cores. | 1800 MHz (megahertz) |
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) The graphics processing unit (GPU) is used to process and display graphics - 3D effects, games, interfaces and other visual elements. Due to the pipeline architecture, the GPU is many times more efficient in graphics processing than the processor. | Qualcomm Adreno 610 |
| GPU clock speed Clock speed is the number of operations per second that the GPU or its core is capable of achieving. The higher the frequency, the higher the speed of the processor, and therefore the number of tasks it can solve. | 600 MHz (megahertz) |
Random access memory (RAM)
| Amount of random access memory (RAM) RAM (Random Access Memory, RAM, RAM) is temporary memory (works only while the device is running), which stores data and code for the operational operation of programs and applications. The more RAM, the more programs you can run simultaneously without loss of performance (there will be fewer “brakes”). | 4 GB (gigabytes) |
| Type of random access memory (RAM) Information about the type of RAM used by the device. | LPDDR4X |
| Number of RAM channels 1 is a single-channel RAM operating mode, basic, when 1 memory module is used. 2 is already a two-channel mode - a mode of parallel operation of 2 modules or pairs of modules, memory channels - this mode is 2 times faster than a single-channel one. 3 – three-channel mode is 3 times faster than single-channel mode. | Dual channel |
| RAM frequency The frequency of RAM determines the speed of RAM, or rather the speed of data transfer and reception. In theory, the higher the frequency, the more powerful the RAM. | 1866 MHz (megahertz) |
Built-in memory
Most mobile devices have built-in Flash memory, which is used as a storage for system data, the operating system, as well as user data - photos, videos, recordings and much more.
| Built-in memory capacity The higher the amount of built-in memory, the more games, programs, music, videos and your other files will fit in the device, especially the amount of memory is important when the device does not support memory cards. | 128 GB (gigabytes) —- UFS 2.1 |
Operating system
A mobile operating system (OS) is pre-installed software with a well-thought-out interface for user control of device functions.
| Operating system (OS) The operating system installed by default by the device manufacturer, as well as its version. | Android 11 |
Battery
To operate autonomously, a mobile device requires a battery that powers all its components.
| Battery capacity The main characteristic of a battery is its maximum capacity, that is, the charge it can store. Capacity is measured in mAh (mAh, milliamp-hour). The higher the capacity, the longer the mobile device can work. | 5000 mAh (milliamp-hours) |
| Battery type Many types of batteries have been used in portable devices, but NiCd (nickel-cadmium), NiMH (nickel-metal hydride), and even more so SLA (lead-acid) batteries are already considered obsolete. Instead, modern mobile devices use Li-Ion (lithium-ion) and Li-Pol, Li-Poly (lithium-polymer) batteries. | Li-Ion (Lithium-ion) |
| Power adapter Characteristics of the charger (adapter, power supply) included in the standard package of the mobile device. More precisely, the output voltage in volts (V) and the output current in amperes (A). | 5 V (volts) / 2 A (amps) |
| Fast charging Fast charging is when the device charges very quickly. For example, up to 50-70% of a full battery charge in ten minutes. | Yes |
Screen
The screen (display) is the main element for displaying graphic information.
| Technology The technology used to make the screen. There are many types of display manufacturing with their pros and cons. | IPS |
| Diagonal The screen diagonal of a device is measured in inches (inch, in or simply ″), and 1″ is equal to 2.54 cm. | 6.5 in (inches) 165.1 mm (millimeters) 16.51 cm (centimeters) |
| Width Approximate screen width | 67.75 mm (millimeters) 6.78 cm (centimeters) |
| Height Approximate screen height | 150.56 mm (millimeters) 15.06 cm (centimeters) |
| Aspect Ratio Aspect ratio is the ratio of the shorter side of the screen, which is considered to be 1, to the longer side, which is denoted by a decimal fraction indicating the ratio to the short side. | 2.222:1 |
| Screen resolution Screen resolution is the number of horizontal pixels (dots) multiplied by the number of vertical pixels. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. | 720 x 1600 pixels |
| Pixel Density The number of pixels per inch or PPI (pixels per inch) indicates the density of pixels per 1 inch (2.54 cm) of the screen. The higher the PPI, the sharper the image, and the less visible or even invisible “squares and dots” (pixels). | 270 ppi (pixels per inch) 106 ppcm (pixels per centimeter) |
| Color depth Color depth means how many bits are used in 1 pixel to display color (bits per pixel). | 24 bit 16777216 colors |
| Screen area Approximate usable area occupied by the screen on the front of the device. The higher the percentage, the narrower the frames around the display or the smaller the “chin with bangs.” | 81.79% (percent) |
| Touch screen A touch screen is a device that usually covers the display and is a touch input tool. In fact, in mobile devices, the touchscreen is a replacement for the keyboard and mouse. | Yes |
| Touch screen type There are many types of touch screens, with their pros and cons. Mobile devices often use capacitive touchscreens, but technology does not stand still and new types of sensors are appearing. | Capacitive |
| Multi-touch Touch screen support for two or more touches. For example, zooming photos with two fingers. | Yes |
| Impact-resistant protective glass of the display The screen and touchscreen of a mobile device are usually covered with protective tempered glass (sometimes plastic or film is used instead of glass) to protect the display from impacts and scratches. Many companies are engaged in the production of such protection, but the most famous are Corning - Gorilla Glass and Asahi - Dragontrail. | Yes |
Main camera
The main camera, usually built into the rear of the device, is designed for creating photo and video content.
| Maximum image resolution This is the maximum number of pixels (dots) horizontally and vertically. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. Resolution can also be indicated in megapixels - this is the total number of pixels that can be in the image, calculated by the formula: vertical pixels multiplied by the number of horizontal pixels and divide the resulting amount by 1 million. | 8000 x 6000 pixels 48 MP (megapixels) |
| Matrix type There are two main types of photomatrix, CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complimentary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor). Mobile devices mainly use a CMOS matrix - it requires less space, has low power consumption and heating. Recently, new types of sensors have begun to appear, for example PureCel from OmniVision. | CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) |
| Matrix size The larger the physical dimensions of the sensor, the larger pixels can be installed there or the greater their number, increasing the luminous flux and exposure. That is, the larger the size, the better. | 1/2″ |
| Matrix pixel size Pixel size is one of the matrix parameters that determines what size pixels are used in the matrix. The larger the size, the better - less noise and a larger light-sensitive area. | 0.8 µm (micrometers) 0.000800 mm (millimeters) |
| Diaphragm Aperture (f-number, f) is used to control the light flux passing through the lens. The aperture is indicated by a fraction, and the smaller the fractional number, the higher the aperture passing through the lens. The more light that passes through the lens, the better overall, less noise in your photos and better night photography. | f/1.7 |
| Flash type Most mobile devices are equipped with light-emitting diode (LED) flashes, but there are also xenon flashes. As a flash, xenon is better - it is more powerful, but LED is more versatile (can work as a flashlight) and consumes less electricity. | Double LED |
| Maximum video resolution This is the maximum number of pixels (dots) horizontally and vertically. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. | 1920 x 1080 pixels 2.07 MP (megapixels) |
| FPS video recording at maximum resolution FPS (Frames per Second, frame rate) is the number of frames that changes in 1 second. The higher the number of frames per second, the smoother the image will be. In this case, we mean the number of frames that the camera can achieve at its maximum resolution; the lower the resolution, the higher the FPS can be. | 60 fps (frames per second) |
| Presence of flash Incorporating a flash into a mobile device allows you to take pictures in low light conditions. Creates the necessary lighting and compensates for the lack of natural light. | Yes |
| Digital zoom With digital zoom (zoom, enlargement), the subject is brought closer due to software image algorithms. The higher the magnification with digital zoom, the worse the image quality (noise, blur) will be compared to a non-zoomed one. | Yes |
| Focus on face Function of auto-detection of living objects and autofocus on their face or head. | Yes |
| Panoramic shooting mode Panoramic photography is a series of frames where each subsequent frame is a continuation of the previous one; at the end of the shooting, all frames are stitched together at the software level to create a panoramic photograph. Frames can be shot both vertically and horizontally, and their width can be up to 360 degrees. This type of shooting is used when the camera's viewing angle is not enough to capture the entire scene. | Yes |
| HDR shooting mode HDR photography takes a quick series of shots with highlights, midtones, and shadows, then combines them into a single frame with high dynamic range. | Yes |
| Electronic (digital) image stabilizer EIS (Electronic Image Stabilizer - digital image stabilization) is performed using software algorithms and is needed to reduce blurring when the camera shakes. | Yes |
| White balance White balance is a setting that helps ensure the correct color reproduction in an image by determining the color temperature of the light source in the frame. The balance can be set either automatically or manually. | Yes |
| ISO Setting ISO is the level of light sensitivity. The lower the ISO, the less sensitive the camera's light sensor and the smoother the image with less noise. The higher the ISO, the higher the light sensitivity, but more noise, graininess, or decreased sharpness. | Yes |
| Additional Information Additional information about the functions and characteristics of cameras. | Autofocus Continuous shooting Geo-tagging Touch focus Exposure compensation Self-timer Scene selection mode Phase detection autofocus (PDAF) Laser autofocus (LAF) |
Additional cameras
Secondary cameras allow you to expand the capabilities of the main camera, such as adding a wide shooting angle, sharpness, optical zoom and other functions depending on the type of secondary camera.
| Second additional camera | 2 MP (megapixels) f/2.4 (aperture) |
| Third additional camera | 2 MP (megapixels) f/2.4 aperture |
Front-camera
The front camera of a mobile device (selfie camera, rear camera) is a camera on the front part, which is usually used for video communication, recognition of gestures or faces, and selfie photographs.
| Photo resolution The maximum image resolution that the camera can produce. As resolution increases, image detail increases. Resolution can also be indicated in megapixels (the total number of pixels that an image can consist of) - these are vertical pixels multiplied by horizontal pixels and divided by 1 million. | 3264 x 2448 pixels 7.99 MP (megapixels) |
| Matrix type There are not many types of matrices, the main ones are CCD, PureCel and the most popular in mobile devices due to low power consumption and compact size - CMOS. | CMOS BSI (backside illumination) |
| Diaphragm An aperture (or aperture) is essentially an adjustable baffle to control the amount of light passing through the lens. The aperture is indicated by a fraction, and the smaller it is, the more light passes through the lens, which has a positive effect on photographs - there will be less noise and better night photography. While the main cameras also come with an adjustable aperture, most front cameras have a fixed aperture. | f/2.2 |
| Video resolution This is the maximum resolution the camera can record video at. The higher the resolution, the better. | 1920 x 1080 pixels 2.07 MP (megapixels) |
| Frame rate (FPS) of video shooting This is talking about FPS at maximum video resolution; at lower resolutions, the frame rate per second can be higher. FPS determines the smoothness of the video, as well as the ability to speed up or slow down it. | 30 fps (frames per second) |
| Face unlock This is a new way to unlock your phone using facial recognition | Yes |
| Additional Information Additional information about the functions and characteristics of cameras. |
Memory card
A memory card (flash card) is an external data storage device that is used in many devices to increase memory capacity.
| Memory card type and formats Mobile devices usually use 3 types of memory cards - SD, miniSD and the most common microSD. Each type has its own formats that the device supports. | microSD microSDHC microSDXC |
SIM card
Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) used in mobile devices to identify subscribers in cellular networks.
| Type, size of SIM card A regular (mini SIM) card has dimensions of 25x15 mm. Micro SIM - 15x12 mm. Nano SIM - 12.3x8.8 mm. The sizes of SIM cards are different and not interchangeable. There is also an eSIM (virtual, electronic SIM card), it is built into the device and does not take up space. | Nano-SIM (4FF - fourth form factor, since 2012, 12.30 x 8.80 x 0.67 mm) Nano-SIM / microSD |
| Number of SIM cards How many SIM cards does the device support? | 2 |
| Additionally Additional information about the operation of SIM cards in the device. | Dual SIM stand-by (Both cards are active. When one is busy talking, the other is deactivated.) |
Mobile networks
This is a system in which communication and data transfer is carried out between subscribers, the location of one or more of which changes. This section lists the supported mobile communication standards and frequencies.
| GSM GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standard for digital mobile cellular communications of the second generation 2G with time and frequency division of channels. GSM came to replace analog cellular communications 1G (first generation). | GSM 850 MHz (B5) GSM 900 MHz (B8) GSM 1800 MHz (B3) |
| LTE LTE (Long-Term Evolution, often referred to as 4G LTE) is a standard for wireless high-speed data transmission, which, although it belongs to fourth generation networks (4G), is essentially a transitional stage from 3G to 4G, greatly accelerating data transfer speeds. The standard has an improved version, LTE Advanced (LTE-A), which can already be considered a full-fledged 4th generation network. | LTE-FDD 700 MHz (B28) LTE-FDD 700 MHz (B29) LTE-FDD 800 MHz (B20) LTE-FDD 850 MHz (B5) LTE-FDD 850 MHz (B18) LTE-FDD 850 MHz (B19) LTE- FDD 850 MHz (B26) LTE-FDD 900 MHz (B8) LTE-FDD 1700 MHz (B4) LTE-FDD 1800 MHz (B3) LTE-FDD 2100 MHz (B1) LTE-FDD 2600 MHz (B7) LTE-TDD 2300 MHz (B40) LTE-TDD 2500 MHz (B41) LTE-TDD 2600 MHz (B38) |
| WCDMA WCDMA (W-CDMA, Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) is a third generation mobile communication standard (3G), which is an add-on to GSM and provides high-speed Internet access. | W-CDMA 850 MHz (B5) W-CDMA 900 MHz (B8) W-CDMA 900 MHz (B19) W-CDMA 1700 MHz (B4) W-CDMA 2100 MHz (B1) |
Mobile network data standards
What data transfer standards in cellular networks are supported by the device, as well as their speed.
| Data transmission technologies Technologies for receiving and transmitting data, as well as their maximum speed. | UMTS (384 kbit/s) EDGE GPRS HSPA+ (HSUPA 5.76 Mbit/s, HSDPA 42 Mbit/s) EV-DO Rev. A (1.8 Mbit/s, 3.1 Mbit/s) LTE Cat 13 DL/Cat 5 UL |
WiFi
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) is a technology for wireless data transmission over a local network among devices based on IEEE 802.11 standards.
| Wi-Fi Direct support The Wi-Fi Direct protocol allows multiple devices to connect directly, bypassing the use of routers or access points. | Yes |
| Wi-Fi Hot-Spot A hotspot is a Wi-Fi access point. In a mobile device, Hot-Spot turns the smartphone into a Wi-Fi access point, essentially turning it into a router capable of distributing the Internet. | Yes |
| WiFi Supported WIFI wireless network standards. | 802.11b (IEEE 802.11b-1999) 802.11g (IEEE 802.11g-2003) 802.11n (IEEE 802.11n-2009) |
Bluetooth
Bluetooth (BT, bluetooth (z), “blue tooth”) is a short-range wireless network (up to 10, sometimes 100 meters) operating on radio waves to transmit voice and data between devices.
| Bluetooth version Bluetooth technology is actively developing and, since 1998, has been constantly updating versions of the standard. Each subsequent version introduces one or several improvements in data exchange speed, range, facilitates pairing, reduces power consumption, or introduces some new protocols and operating profiles. The higher the Bluetooth version, the better. The technology is also backward compatible, for example, if your mobile device has version 5.0, then it will work with accessories version 4.2 and lower, but the improvements introduced in version 5.0 will not work; they will work only if both the device and accessories are version 5. | 5.0 |
| Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Bluetooth LE is a low energy BT protocol specification. | Yes |
| A2DP profile The A2DP Bluetooth profile is designed to transmit a high-quality two-channel stereo signal via Bluetooth to wireless headphones, speakers and other acoustics. | Yes |
Sensors
Modern devices have many sensors that help in measurements, trigger functions, and make using the device more pleasant.
| Light sensor The light sensor reacts to the light level and is able to adjust the screen brightness automatically based on this. This is necessary to reduce power consumption and ease of use of the device. | Yes |
| Proximity sensor The proximity sensor reacts to the proximity of the mobile device to some object. For example, the sensor is used when talking on the phone to turn off the screen, which saves energy and prevents you from pressing buttons with your ear or cheek. | Yes |
| Gyroscope Gyroscope (gyroscope, gyro sensor) is a sensor for orientation in space that tracks the angle of inclination of even a stationary device along three coordinate axes. The sensor is mainly used in conjunction with an accelerometer in games and applications. | Yes |
| Accelerometer An accelerometer is a sensor that measures apparent acceleration, that is, it determines the position and distance at which a mobile device moves in space. Based on the data from this sensor, the screen orientation change, pedometer, control using tilts and gestures in games and applications, etc. work. | Yes |
| Fingerprint's scanner The scanner is responsible for authorization using a previously saved fingerprint, as a result of which the device is unlocked, payment is made, some action is confirmed - just put your finger on the scanner. Scanners can be either built into the body or built into a button or screen. | Yes |
| Digital compass This is software that displays data from a magnetic sensor or GPS in the form of a compass on the screen of a mobile device. If there are no sensors or GPS, then the digital compass will not work. | Yes |
| Additional sensors |
Audio
Audio - characteristics and capabilities of a mobile device in terms of sound.
| Music speaker There are two types of speakers in mobile devices - auditory and musical. The auditory speaker (speaker) is used for conversation, the music speaker (buzzer) is used to play music and sounds. | Loudspeaker Earphone —- Dual microphone noise cancellation |
Radio
The radio in a mobile device can be built-in by the manufacturer (catch local radio channels, no internet required, often works only with headphones (as an antenna), but not always) or installed as an online application (requires internet, but more channels and often better quality) .
| Built-in radio Is a radio tuner integrated into the mobile device? | Yes |
Navigation and location
The location is determined by satellite navigation systems that track the device's autonomous geospatial location at multiple points. The most common satellite navigation systems are GPS, GLONASS, and the Chinese BeiDou.
| GPS GPS (Global Positioning System) is a global satellite navigation system that can determine the position of a mobile device, build routes and find the desired object on the map with an accuracy of several meters. | Yes |
| A-GPS A-GPS (Assisted GPS) is an assistive technology that will help you quickly find the location of your cellular device without waiting for satellite data, which is especially important in indoors and cities. Location is determined in various ways, for example, Wi-Fi access points, mobile towers, bluetooth and others. | Yes |
| GLONASS GLONASS is a Russian Global Navigation Satellite System, which is similar to GPS and works in tandem with it, increasing the accuracy and speed of navigation. | Yes |
| Additional navigation systems | BeiDou Galileo LTEPP SUPL |
USB connector
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a serial interface for connecting peripherals to computers, smartphones, laptops and much more. The interface allows you to exchange data and power a peripheral device with energy, as well as connect several peripheral devices to one USB connector at once.
| Connector type What type of USB connector is used in the device. | Micro USB |
| USB standard The higher the standard, the faster the throughput, or more precisely the data exchange rate. With version 3.0 of the standard, the current was increased to 0.9A, eliminating the need for additional power for some devices. | 2.0 |
| USB Mass Storage Connecting a mobile device via USB as a data storage device. That is, when you enable this mode, your device can be used as a flash drive. | Yes |
| USB OTG support OTG is the ability to connect peripherals, such as keyboards and mice, flash drives, card readers, and much more, to the USB port of your device via an adapter or directly. You can connect devices that do not require specialized drivers or additional power. | Yes |
| Additional characteristics Additional features of the USB connector, for example, OTG, whether the connection is supported, peripheral devices and additional memory. | Charging via USB |
Headphone jack
A TRS headphone jack (or jack) is a common standard of connectors used for transmitting audio signals. By diameter there are jack (6.5 mm), mini-jack (3.5 mm) and micro-jack (2.5 mm). In mobile devices, the 3.5mm jack was considered the most popular and widespread, but recently they began to be removed, leaving only USB connectors, through which headphones are connected with a corresponding plug or using adapters.
| 3.5mm headphone jack Does the device have a 3.5 mm audio jack? | Yes |
Connection and synchronization
Options for synchronizing your mobile device and connecting it to other devices.
| NFC NFC (Near field communication, near contactless communication) is a technology for contactless communication between devices over a short distance. Widely used for contactless payment, in the form of a travel card or pass, and is also used for reading and interacting with NFC tags and for exchanging data between devices. | Yes |
| Connection, synchronization Types of synchronization and connection technologies supported by the device. | Computer sync OTA sync Tethering VoLTE |
Browser
A browser is a browser program for viewing sites and their content on the Internet. Through the browser, you can open websites, search for information, download necessary files, watch streaming videos, play browser games, etc.
| Technologies Markup and programming languages supported by the built-in (standard) browser. For mobile devices, you can install additional browser applications if the standard one does not suit you. | HTML HTML5 CSS 3 |
Audio file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support many audio file formats, as well as codecs for playing them.
| Default formats The formats that the mobile device supports out of the box are indicated. But if the device does not support the format you need, then you can try adding support for it. Sometimes support depends on the technical characteristics of the device (“hardware”) and nothing can be added here, but often the ability to process a particular audio format depends on the software part. You can install another audio player or codec set separately. | AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) AMR / AMR-NB / GSM-AMR (Adaptive Multi-Rate, .amr, .3ga) aptX / apt-X eAAC+ / aacPlus v2 / HE-AAC v2 FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec, .flac ) MIDI MP3 (MPEG-2 Audio Layer II, .mp3) OGG (.ogg, .ogv, .oga, .ogx, .spx, .opus) WMA (Windows Media Audio, .wma) WAV (Waveform Audio File Format, .wav, .wave) |
Video file formats/codecs
Video file formats that the device supports and is capable of decoding and playing.
| Default formats Video file formats that the device is capable of playing with standard firmware and a standard (built-in) set of programs. Not all formats are supported by default, but you can install a third-party video player and/or set of codecs. | 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project, .3gp) AVI (Audio Video Interleaved, .avi) H.263 H.264 / MPEG-4 Part 10 / AVC video MKV (Matroska Multimedia Container, .mkv .mk3d .mka .mks) QuickTime (.mov, .qt) MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14, .mp4, .m4a, .m4p, .m4b, .m4r, .m4v) WebM WMV (Windows Media Video, .wmv) Xvid |
How to unlock iPhone
If you have forgotten the password for your iOS device, you have only one option - reset to factory settings. You can do it in two ways: using iCloud and through iTunes. The first one will only work if you previously enabled the Find My iPhone function on your smartphone. For the second, you will need a USB cable and a computer with iTunes installed.
In both cases, you will not only delete the password, but also all data from the device. But if you have a backup of your iPhone, then after resetting you can restore the information saved in it: calendars, contacts, notes, SMS, settings and shopping lists in iTunes and the App Store. Personal photos and videos will also not be lost if you previously synchronized them with your computer or iCloud.
Reset iPhone to factory settings using iCloud
To check if Find My iPhone is active on your smartphone, connect it to the Internet. Then log into your Apple ID account on the iCloud website using your computer and click on the “Find iPhone” icon.
If you don't have a computer at hand, but have an iPad, iPod touch, or another iPhone, you can use the standard Find My iPhone application on any of these gadgets. It works the same as the web version in iCloud.
If Find My iPhone is active, you'll immediately see your locked iPhone (in the app) or select it from the All Devices list (on the iCloud website). If the device is not displayed, proceed to the second method. Otherwise, continue.
Click on the smartphone icon, and then on the “Erase iPhone” button and follow further prompts.
This will remove your passcode and all data from your device, allowing you to set up your iPhone again.
Reset your iPhone to factory settings via iTunes
Launch iTunes on your computer, then connect your smartphone to it using a USB cable.
If you have previously synced your iPhone with this computer, click on the smartphone icon in iTunes. In the menu that opens, sync again and create a fresh backup of the device on your computer. Then click “Restore from copy...”, select the newly created image and follow the system prompts until complete recovery.
If you've never synced your iPhone with your current computer, or iTunes also asks for a password, then most likely you won't be able to create a new backup. But you can do a reset in a special mode, and then restore the device from old copies (if any). Follow these steps to reset:
1. Force restart your iPhone.
On iPhone SE, iPhone 6s, iPhone 6s Plus, and older models, hold down the Home key and the top (or side) button for 10 seconds or more until the recovery screen appears.
On an iPhone 7 or iPhone 7 Plus, hold down the Side key and the Volume Down button for 10 seconds or more until you see the recovery screen.
On an iPhone 8 or iPhone 8 Plus, hold and immediately release the volume up key and then the volume down key. After that, press and hold the Side button until the recovery screen appears.
2. When the recovery dialog box appears on your computer display, click “Restore” and follow the iTunes prompts.
3. If the iPhone exits recovery mode while iTunes is downloading the necessary files from the Internet, press and hold the force restart buttons again until the device returns to this mode.
Although the instructions for both reset methods are based on the iPhone, they will also work if you suddenly forget your iPad password.