The Lenovo A536 phone is one of the most interesting mobile gadgets today. Its reliable operation is guaranteed by timely updating of applications and software platform. Firmware for smartphones is used specifically for this purpose.
You can use the standard version of the firmware, and if it supports the self-updating function, this may be enough for full operation. But if an independent update does not occur or there are some system failures in the operation of the gadget, it is quite appropriate to replace the firmware version yourself with some other one.
There are two ways to install new firmware on the Lenovo a536: either through an additional program from a computer, or through the Recovery system on the phone itself. You will be pleased with the results in both cases if you follow the instructions below.
Preparing for firmware
Before you learn how to reflash a Lenovo phone, it is important to understand what preliminary steps you should definitely take:
- Download the firmware version you need. As a rule, it is downloaded as an archive, so unzip the file and place it in a convenient place:
- Official firmware A536 S186 150813 (892MB).
- Charge the battery to at least half of its total capacity. It is best to have the battery fully charged.
- Check for the latest USB drivers on your computer to connect your phone to it:
- Driver for advanced operation of a smartphone with a PC (modem mode, USB debugging mode, etc.) - ;
- Special mode driver - mode driver for flashing smartphone firmware from a PC (auto-installer) x86/x64 - .
Detailed technical specifications
Make and model
Make and model of the device, and alternative names (if any).
| Brand Device manufacturer company. | Lenovo |
| Model Device name. | A536 |
Design
Appearance of the device including dimensions, weight, volume, colors and materials.
| Width The horizontal side of the device when used in standard orientation. | 72 mm (millimeters) |
| Height The vertical side of the device when used in standard orientation. | 139.6 mm (millimeters) |
| Thickness The cross-sectional size of the device. | 9.95 mm (millimeters) |
| Weight How much does the device weigh excluding the case, SIM and memory cards and other additional elements. | 148 g (grams) |
| Volume Approximate value calculated using the formula: length times width times height. | 100.01 cm³ (cubic centimeters) |
| Colors What colors is the device available in? | Black White |
| Housing materials What materials is the body made of? | Plastic |
System on a Chip (SoC)
A system on a chip, a single-chip system (System on a Chip, SoC) is when several systems performing different device functions are connected on one chip.
| System on a Chip (SoC) A single-chip system that contains components such as a processor, graphics accelerator, memory units, communication interfaces, etc., as well as software for the operation of the system. | MediaTek MT6582M |
Central processing unit (CPU)
| Central processing unit (CPU) The main component of the device is responsible for calculations and data processing. | ARM Cortex-A7 |
| Technical process What technological process is used to make the chip? The smaller the process technology, the better - the chips consume less power and generate less heat. | 28 nm (nanometers) |
| Processor size Processor capacity is a parameter that indicates how many bits of data a processor register processes in 1 clock cycle. This is usually 32 or 64 bits. | 32 bit |
| Instruction Set Architecture Instruction set architecture (ISA) is a programmable part of the microprocessor core used by software to control the operation of the processor. | ARMv7 |
| Number of processor cores The processor can be either single-core or multi-core. The performance of the processor depends on the number of cores (threads). The more cores working simultaneously, the higher the power consumption, so in mobile devices all cores are used only under high load. | 4 |
| CPU clock speed Clock speed is the number of operations per second that a processor or its core can achieve. The higher the frequency, the higher the overall performance of the device, but performance also depends on the processor architecture and the number of cores. | 1300 MHz (megahertz) |
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
| Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) The graphics processing unit (GPU) is used to process and display graphics - 3D effects, games, interfaces and other visual elements. Due to the pipeline architecture, the GPU is many times more efficient in graphics processing than the processor. | ARM Mali-400 MP2 |
| Number of GPU cores Similar to a processor, a GPU can have one core or several. The number of cores (threads) determines the performance and amount of information processed. The more cores, the better. | 2 |
| GPU clock speed Clock speed is the number of operations per second that the GPU or its core is capable of achieving. The higher the frequency, the higher the speed of the processor, and therefore the number of tasks it can solve. | 416 MHz (megahertz) |
Random access memory (RAM)
| Amount of random access memory (RAM) RAM (Random Access Memory, RAM, RAM) is temporary memory (works only while the device is running), which stores data and code for the operational operation of programs and applications. The more RAM, the more programs you can run simultaneously without loss of performance (there will be fewer “brakes”). | 1 GB (gigabytes) |
| Number of RAM channels 1 is a single-channel RAM operating mode, basic, when 1 memory module is used. 2 is already a two-channel mode - a mode of parallel operation of 2 modules or pairs of modules, memory channels - this mode is 2 times faster than a single-channel one. 3 – three-channel mode is 3 times faster than single-channel mode. | Single channel |
| RAM frequency The frequency of RAM determines the speed of RAM, or rather the speed of data transfer and reception. In theory, the higher the frequency, the more powerful the RAM. | 533 MHz (megahertz) |
Built-in memory
Most mobile devices have built-in Flash memory, which is used as a storage for system data, the operating system, as well as user data - photos, videos, recordings and much more.
| Built-in memory capacity The higher the amount of built-in memory, the more games, programs, music, videos and your other files will fit in the device, especially the amount of memory is important when the device does not support memory cards. | 8 GB (gigabytes) |
Operating system
A mobile operating system (OS) is pre-installed software with a well-thought-out interface for user control of device functions.
| Operating system (OS) The operating system installed by default by the device manufacturer, as well as its version. | Android 4.4.2 KitKat |
Battery
To operate autonomously, a mobile device requires a battery that powers all its components.
| Battery capacity The main characteristic of a battery is its maximum capacity, that is, the charge it can store. Capacity is measured in mAh (mAh, milliamp-hour). The higher the capacity, the longer the mobile device can work. | 2000 mAh (milliamp-hours) |
| Battery type Many types of batteries have been used in portable devices, but NiCd (nickel-cadmium), NiMH (nickel-metal hydride), and even more so SLA (lead-acid) batteries are already considered obsolete. Instead, modern mobile devices use Li-Ion (lithium-ion) and Li-Pol, Li-Poly (lithium-polymer) batteries. | Li-polymer |
| Call duration on 2G network (GSM, CDMA) Approximately how long will it take for a fully charged battery to discharge when talking in 2G mode. Approximate, because this time is influenced by many factors, such as the operator, signal strength, active applications, and so on. | 15 hours 30 minutes 15.5 hours (hours) 930 minutes (minutes) 0.6 days |
| Waiting time on 2G network (GSM, CDMA) Approximately how long will it take for a fully charged battery to discharge if the mobile device is not used and is connected in 2G mode. | 300 h (hours) 18000 min (minutes) 12.5 days |
| Call duration on 3G network (WCDMA, UMTS, CDMA2000) About how long a fully charged battery will be discharged during a call on third generation networks. Approximate time because it is influenced by various factors, including ambient temperature. | 12 h (hours) 720 min (minutes) 0.5 days |
| Waiting time on 3G network (WCDMA, UMTS, CDMA2000) About how long a fully charged battery will be discharged if the mobile device is in standby mode and connected to third generation networks. | 300 h (hours) 18000 min (minutes) 12.5 days |
Screen
The screen (display) is the main element for displaying graphic information.
| Technology The technology used to make the screen. There are many types of display manufacturing with their pros and cons. | TFT |
| Diagonal The screen diagonal of a device is measured in inches (inch, in or simply ″), and 1″ is equal to 2.54 cm. | 5 in (inches) 127 mm (millimeters) 12.7 cm (centimeters) |
| Width Approximate screen width | 62.23 mm (millimeters) 6.22 cm (centimeters) |
| Height Approximate screen height | 110.71 mm (millimeters) 11.07 cm (centimeters) |
| Aspect Ratio Aspect ratio is the ratio of the shorter side of the screen, which is considered to be 1, to the longer side, which is denoted by a decimal fraction indicating the ratio to the short side. | 1.779:1 |
| Screen resolution Screen resolution is the number of horizontal pixels (dots) multiplied by the number of vertical pixels. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. | 480 x 854 pixels |
| Pixel Density The number of pixels per inch or PPI (pixels per inch) indicates the density of pixels per 1 inch (2.54 cm) of the screen. The higher the PPI, the sharper the image, and the less visible or even invisible “squares and dots” (pixels). | 196 ppi (pixels per inch) 77 ppcm (pixels per centimeter) |
| Color depth Color depth means how many bits are used in 1 pixel to display color (bits per pixel). | 24 bit 16777216 colors |
| Screen area Approximate usable area occupied by the screen on the front of the device. The higher the percentage, the narrower the frames around the display or the smaller the “chin with bangs.” | 68.76% (percent) |
| Touch screen A touch screen is a device that usually covers the display and is a touch input tool. In fact, in mobile devices, the touchscreen is a replacement for the keyboard and mouse. | Yes |
| Touch screen type There are many types of touch screens, with their pros and cons. Mobile devices often use capacitive touchscreens, but technology does not stand still and new types of sensors are appearing. | Capacitive |
| Multi-touch Touch screen support for two or more touches. For example, zooming photos with two fingers. | Yes |
Main camera
The main camera, usually built into the rear of the device, is designed for creating photo and video content.
| Maximum image resolution This is the maximum number of pixels (dots) horizontally and vertically. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. Resolution can also be indicated in megapixels - this is the total number of pixels that can be in the image, calculated by the formula: vertical pixels multiplied by the number of horizontal pixels and divide the resulting amount by 1 million. | 2592 x 1944 pixels 5.04 MP (megapixels) |
| Matrix type There are two main types of photomatrix, CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) and CMOS (Complimentary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor). Mobile devices mainly use a CMOS matrix - it requires less space, has low power consumption and heating. Recently, new types of sensors have begun to appear, for example PureCel from OmniVision. | CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) |
| Flash type Most mobile devices are equipped with light-emitting diode (LED) flashes, but there are also xenon flashes. As a flash, xenon is better - it is more powerful, but LED is more versatile (can work as a flashlight) and consumes less electricity. | LED |
| Maximum video resolution This is the maximum number of pixels (dots) horizontally and vertically. The higher the resolution, the more detailed the image will be. | 1920 x 1088 pixels 2.09 MP (megapixels) |
| FPS video recording at maximum resolution FPS (Frames per Second, frame rate) is the number of frames that changes in 1 second. The higher the number of frames per second, the smoother the image will be. In this case, we mean the number of frames that the camera can achieve at its maximum resolution; the lower the resolution, the higher the FPS can be. | 30 fps (frames per second) |
| Presence of flash Incorporating a flash into a mobile device allows you to take pictures in low light conditions. Creates the necessary lighting and compensates for the lack of natural light. | Yes |
| Digital zoom With digital zoom (zoom, enlargement), the subject is brought closer due to software image algorithms. The higher the magnification with digital zoom, the worse the image quality (noise, blur) will be compared to a non-zoomed one. | Yes |
| Focus on face Function of auto-detection of living objects and autofocus on their face or head. | Yes |
| Panoramic shooting mode Panoramic photography is a series of frames where each subsequent frame is a continuation of the previous one; at the end of the shooting, all frames are stitched together at the software level to create a panoramic photograph. Frames can be shot both vertically and horizontally, and their width can be up to 360 degrees. This type of shooting is used when the camera's viewing angle is not enough to capture the entire scene. | Yes |
| HDR shooting mode HDR photography takes a quick series of shots with highlights, midtones, and shadows, then combines them into a single frame with high dynamic range. | Yes |
| Electronic (digital) image stabilizer EIS (Electronic Image Stabilizer - digital image stabilization) is performed using software algorithms and is needed to reduce blurring when the camera shakes. | Yes |
| ISO Setting ISO is the level of light sensitivity. The lower the ISO, the less sensitive the camera's light sensor and the smoother the image with less noise. The higher the ISO, the higher the light sensitivity, but more noise, graininess, or decreased sharpness. | Yes |
| Additional Information Additional information about the functions and characteristics of cameras. | Autofocus Geo-tagging Touch focus |
Front-camera
The front camera of a mobile device (selfie camera, rear camera) is a camera on the front part, which is usually used for video communication, recognition of gestures or faces, and selfie photographs.
| Photo resolution The maximum image resolution that the camera can produce. As resolution increases, image detail increases. Resolution can also be indicated in megapixels (the total number of pixels that an image can consist of) - these are vertical pixels multiplied by horizontal pixels and divided by 1 million. | 1600 x 1200 pixels 1.92 MP (megapixels) |
Memory card
A memory card (flash card) is an external data storage device that is used in many devices to increase memory capacity.
| Memory card type and formats Mobile devices usually use 3 types of memory cards - SD, miniSD and the most common microSD. Each type has its own formats that the device supports. | microSD microSDHC |
SIM card
Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) used in mobile devices to identify subscribers in cellular networks.
| Type, size of SIM card A regular (mini SIM) card has dimensions of 25x15 mm. Micro SIM - 15x12 mm. Nano SIM - 12.3x8.8 mm. The sizes of SIM cards are different and not interchangeable. There is also an eSIM (virtual, electronic SIM card), it is built into the device and does not take up space. | Mini-SIM (2FF - second form factor, since the late 1990s, 25.00 x 15.00 x 0.76 mm) |
| Number of SIM cards How many SIM cards does the device support? | 2 |
Mobile networks
This is a system in which communication and data transfer is carried out between subscribers, the location of one or more of which changes. This section lists the supported mobile communication standards and frequencies.
| GSM GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standard for digital mobile cellular communications of the second generation 2G with time and frequency division of channels. GSM came to replace analog cellular communications 1G (first generation). | GSM 900 MHz GSM 1800 MHz GSM 1900 MHz |
| UMTS UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System), also called 3GSM, is a third generation (3G) mobile communications standard based on the WCDMA air interface. | UMTS 900 MHz UMTS 2100 MHz |
Mobile network data standards
What data transfer standards in cellular networks are supported by the device, as well as their speed.
| Data transmission technologies Technologies for receiving and transmitting data, as well as their maximum speed. | UMTS (384 kbit/s) EDGE GPRS HSPA+ (HSUPA 5.76 Mbit/s, HSDPA 21 Mbit/s) |
WiFi
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity) is a technology for wireless data transmission over a local network among devices based on IEEE 802.11 standards.
| Wi-Fi Hot-Spot A hotspot is a Wi-Fi access point. In a mobile device, Hot-Spot turns the smartphone into a Wi-Fi access point, essentially turning it into a router capable of distributing the Internet. | Yes |
| WiFi Supported WIFI wireless network standards. | 802.11b (IEEE 802.11b-1999) 802.11g (IEEE 802.11g-2003) 802.11n (IEEE 802.11n-2009) |
Bluetooth
Bluetooth (BT, bluetooth (z), “blue tooth”) is a short-range wireless network (up to 10, sometimes 100 meters) operating on radio waves to transmit voice and data between devices.
| Bluetooth version Bluetooth technology is actively developing and, since 1998, has been constantly updating versions of the standard. Each subsequent version introduces one or several improvements in data exchange speed, range, facilitates pairing, reduces power consumption, or introduces some new protocols and operating profiles. The higher the Bluetooth version, the better. The technology is also backward compatible, for example, if your mobile device has version 5.0, then it will work with accessories version 4.2 and lower, but the improvements introduced in version 5.0 will not work; they will work only if both the device and accessories are version 5. | 4.0 |
| A2DP profile The A2DP Bluetooth profile is designed to transmit a high-quality two-channel stereo signal via Bluetooth to wireless headphones, speakers and other acoustics. | Yes |
Sensors
Modern devices have many sensors that help in measurements, trigger functions, and make using the device more pleasant.
| Proximity sensor The proximity sensor reacts to the proximity of the mobile device to some object. For example, the sensor is used when talking on the phone to turn off the screen, which saves energy and prevents you from pressing buttons with your ear or cheek. | Yes |
| Accelerometer An accelerometer is a sensor that measures apparent acceleration, that is, it determines the position and distance at which a mobile device moves in space. Based on the data from this sensor, the screen orientation change, pedometer, control using tilts and gestures in games and applications, etc. work. | Yes |
| Additional sensors |
Audio
Audio - characteristics and capabilities of a mobile device in terms of sound.
| Music speaker There are two types of speakers in mobile devices - auditory and musical. The auditory speaker (speaker) is used for conversation, the music speaker (buzzer) is used to play music and sounds. | Loudspeaker Earphone |
Radio
The radio in a mobile device can be built-in by the manufacturer (catch local radio channels, no internet required, often works only with headphones (as an antenna), but not always) or installed as an online application (requires internet, but more channels and often better quality) .
| Built-in radio Is a radio tuner integrated into the mobile device? | Yes |
Navigation and location
The location is determined by satellite navigation systems that track the device's autonomous geospatial location at multiple points. The most common satellite navigation systems are GPS, GLONASS, and the Chinese BeiDou.
| GPS GPS (Global Positioning System) is a global satellite navigation system that can determine the position of a mobile device, build routes and find the desired object on the map with an accuracy of several meters. | Yes |
| A-GPS A-GPS (Assisted GPS) is an assistive technology that will help you quickly find the location of your cellular device without waiting for satellite data, which is especially important in indoors and cities. Location is determined in various ways, for example, Wi-Fi access points, mobile towers, bluetooth and others. | Yes |
| Additional navigation systems |
USB connector
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a serial interface for connecting peripherals to computers, smartphones, laptops and much more. The interface allows you to exchange data and power a peripheral device with energy, as well as connect several peripheral devices to one USB connector at once.
| Connector type What type of USB connector is used in the device. | Micro USB |
| USB standard The higher the standard, the faster the throughput, or more precisely the data exchange rate. With version 3.0 of the standard, the current was increased to 0.9A, eliminating the need for additional power for some devices. | 2.0 |
| USB Mass Storage Connecting a mobile device via USB as a data storage device. That is, when you enable this mode, your device can be used as a flash drive. | Yes |
| Additional characteristics Additional features of the USB connector, for example, OTG, whether the connection is supported, peripheral devices and additional memory. | Charging via USB |
Headphone jack
A TRS headphone jack (or jack) is a common standard of connectors used for transmitting audio signals. By diameter there are jack (6.5 mm), mini-jack (3.5 mm) and micro-jack (2.5 mm). In mobile devices, the 3.5mm jack was considered the most popular and widespread, but recently they began to be removed, leaving only USB connectors, through which headphones are connected with a corresponding plug or using adapters.
| 3.5mm headphone jack Does the device have a 3.5 mm audio jack? | Yes |
Connection and synchronization
Options for synchronizing your mobile device and connecting it to other devices.
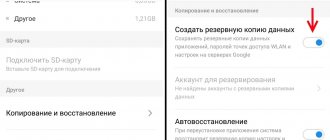
| Connection, synchronization Types of synchronization and connection technologies supported by the device. | Computer sync OTA sync Tethering |
Browser
A browser is a browser program for viewing sites and their content on the Internet. Through the browser, you can open websites, search for information, download necessary files, watch streaming videos, play browser games, etc.
| Technologies Markup and programming languages supported by the built-in (standard) browser. For mobile devices, you can install additional browser applications if the standard one does not suit you. | HTML HTML5 CSS 3 |
Audio file formats/codecs
Mobile devices support many audio file formats, as well as codecs for playing them.
| Default formats The formats that the mobile device supports out of the box are indicated. But if the device does not support the format you need, then you can try adding support for it. Sometimes support depends on the technical characteristics of the device (“hardware”) and nothing can be added here, but often the ability to process a particular audio format depends on the software part. You can install another audio player or codec set separately. | AAC (Advanced Audio Coding) AMR / AMR-NB / GSM-AMR (Adaptive Multi-Rate, .amr, .3ga) MIDI MP3 (MPEG-2 Audio Layer II, .mp3) WMA (Windows Media Audio, .wma) WAV (Waveform Audio File Format, .wav, .wave) |
Video file formats/codecs
Video file formats that the device supports and is capable of decoding and playing.
| Default formats Video file formats that the device is capable of playing with standard firmware and a standard (built-in) set of programs. Not all formats are supported by default, but you can install a third-party video player and/or set of codecs. | 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project, .3gp) AVI (Audio Video Interleaved, .avi) H.263 H.264 / MPEG-4 Part 10 / AVC video MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14, .mp4, .m4a, .m4p , .m4b, .m4r, .m4v) WMV (Windows Media Video, .wmv) |
Step-by-step firmware instructions
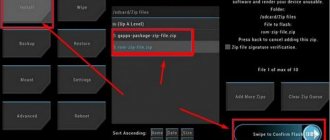
First, let's see how to flash a 536 A smartphone using the FlashTool program:
- We take out the battery from the phone and connect it, switched off, via USB to the computer.
- In the task manager, you will see the phone as an unidentified device. Click on it to update the drivers.
- We activate the firmware mode. After that you will see Mediatek Preloader.
- Disconnect the phone from the computer and launch the exe application.
- Click on the scatter-loading button and select the appropriate file in the scatter format.
- Place a checkmark next to the item DA DL ALL WITH Cheksum that appears. This is necessary so that after the system update you can turn on the phone.
- Click on the DOWNLOAD button to start downloading files.
- If you did everything correctly, then after the successful completion of the procedure you will see a green check mark on the screen.
- Now you can turn on the phone and carry out its initial setup.
How to find out the current Android version on Lenovo A536
Before installing updates, it is recommended to check the current firmware version. It is possible that the latest Android is already installed on your phone, and an update is not required.
To view the current version you need:
- Open your smartphone settings.
- Go to the “About phone” section.
- Find the “Android Version” item.
This section will indicate the current firmware version. At the beginning of 2021, the current OS is Android 10, but very soon Google will release the next Android 11 update.
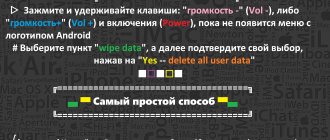
Firmware via recovery
There is an alternative option to flash your phone, and you don’t need a computer to implement it. This is done like this:
- Turn off the smartphone.
- Press and hold the volume up and power buttons at the same time.
- We see the Lenovo logo on the screen. This means that we get access to the recovery system. As soon as this happens, you can release the previously held buttons.
- Click on the “Wipe” button, selecting the first three items from the list that appears.
- Click on “Install” to start updating your phone.
- We wait until the phone reboots and it can be configured.
The advantage of the second method is that the update is carried out without additional software. But, unfortunately, it won’t be possible to change the standard firmware to custom firmware this way.
Don’t be afraid to make changes to the installed smartphone software platform yourself. This is not difficult at all and can be done by any mobile device user. The main thing is to strictly follow the instructions and act carefully. Then any risk of disruption of the smartphone as a result of updating or replacing the firmware can be eliminated.
Description of the advantages and disadvantages of the A536 phone
The Lenovo A536 measures 72 mm wide, 139.6 mm long and 9.95 mm thick. With such dimensions it is convenient to operate the device with one hand. In addition, the weight of the device is about 148 g. Even if you operate the device with one hand, its weight is almost not felt.
If we evaluate the overall ease of use of the phone taking into account the size and weight, then there will be no problems with everyday use.
The smartphone is equipped with a 4-core MediaTek MT6582M processor, which is made at 28 nm. technical process.
The smartphone has only 1 GB. RAM, which is quite small. Instances of low RAM will occur regularly, so even when using light applications you will experience instability in operation.
The storage capacity of the device is 8 GB, and if the smartphone is mainly used for correspondence and social networks, then there will be no problems, but if you are going to use it for photography, video shooting and games, you should look at a device of a higher class.
The phone is compatible with SD cards, so you can easily expand its memory. So you probably don't need to worry about storage capacity.
The A536 has a 5-inch display diagonal. The display is large enough that you will rarely have problems with its size. However, this display is not suitable for writing long texts.
In terms of quality, the screen may appear pixelated when displaying a picture or video. It should be sufficient for normal use.
The main camera of the phone has 5.04 megapixels, which should be enough in most cases. However, you may be slightly unsatisfied with the quality of the photos.
Also, the smartphone has a 1.92 megapixel front camera, which is low. If you care about the quality of your photos, you should consider a higher-end smartphone.
The Lenovo A536 battery capacity is 2000 mAh, which is a common capacity indicator. Compared to other smartphones, the Lenovo A536's battery life is average. You don't have to worry about anything during daily use. However, if you spend time surfing the internet or playing games, you might be a little underwhelmed by the battery life.
Do I need to update the firmware and waste time?
The main point of updates is to eradicate bugs, problems and shortcomings, of which there are plenty in the Android operating system:
- For example, system applications freeze or crash.
- Blurred corners of pictures with a good camera.
- The smartphone does not turn on at all.
- The phone turns off and reboots whenever it wants.
- Heavy power consumption when wi-fi is turned on, for example, the battery runs out in an hour.
- There can be a lot of glitches; there are times when the phone itself starts calling the first number in the phone book. Hardly anyone is happy with this behavior.
There are also ordinary enthusiasts who love everything new and want to test the latest Android.
How to get root rights
In the field of obtaining root rights, there are two universal programs (universal because they support a lot of devices) that get root in 1 click, this is ZYKURoot 2.2 - (site zykuroot.info), maybe there is a newer version, you need to look at this on the site
And Rootkhp Pro 2.6 – (from the Rootkhp pro website). The version may also not be the latest; you need to check their website.
In general, instructions for them are not needed, everything is as usual, connect the phone to the computer and click Root. Then we sit and wait for what the program says.